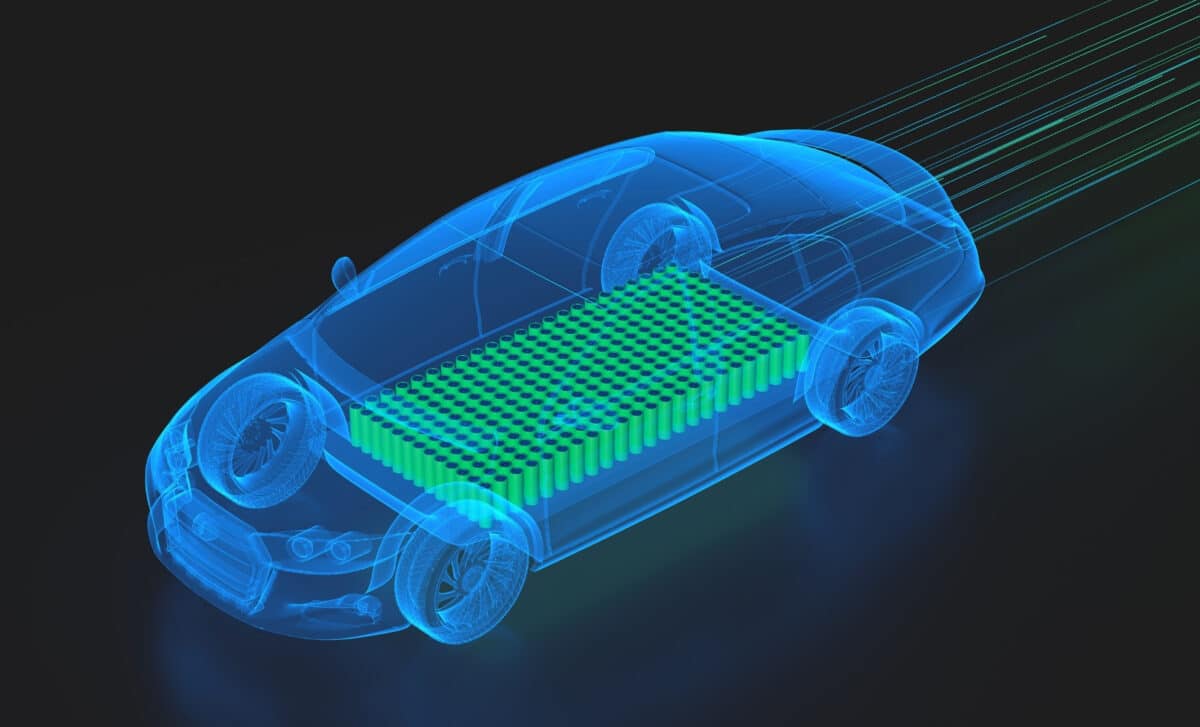
With over a year of research and development already completed, this battery’s potential to significantly extend electric vehicle autonomy is drawing attention across the industry. As the challenges of charging time, range, and battery efficiency remain central to EV adoption, Hongqi’s prototype could set a new standard.
Electric mobility has evolved rapidly in recent years, but battery limitations still pose a barrier to widespread adoption. Range anxiety continues to dominate buyer concerns, especially in markets lacking dense charging infrastructure. Now, one manufacturer is preparing to push past this limit with a new technology that has taken shape over 470 days of dedicated development.
The vehicle at the center of this development is the Hongqi Tiangong 06, the first EV from the brand to be equipped with a semi-solid-state battery. The prototype is already in real-world testing on Chinese roads, following its rollout from production lines. This phase signals the final step before industrialization begins.
First Prototype Marks over a Year of Development
The Hongqi Tiangong 06, which carries this next-generation battery, is the result of sustained work at the FAW R&D center. After nearly a year and a half of development, the vehicle has transitioned from lab to road.
The semi-solid-state technology it uses includes sulfide electrolytes and a battery system fully integrated into the vehicle’s platform. This not only aims to boost range but also battery efficiency. The solid-state format represents a key departure from current lithium-ion designs, focusing on safer and more stable chemistry.
Hongqi is a subsidiary of FAW Group, one of China’s major automotive conglomerates, and this project reflects its ambition to lead the high-range EV sector. The road tests now underway will help validate the battery’s performance under real-world driving conditions, a necessary step before large-scale deployment.
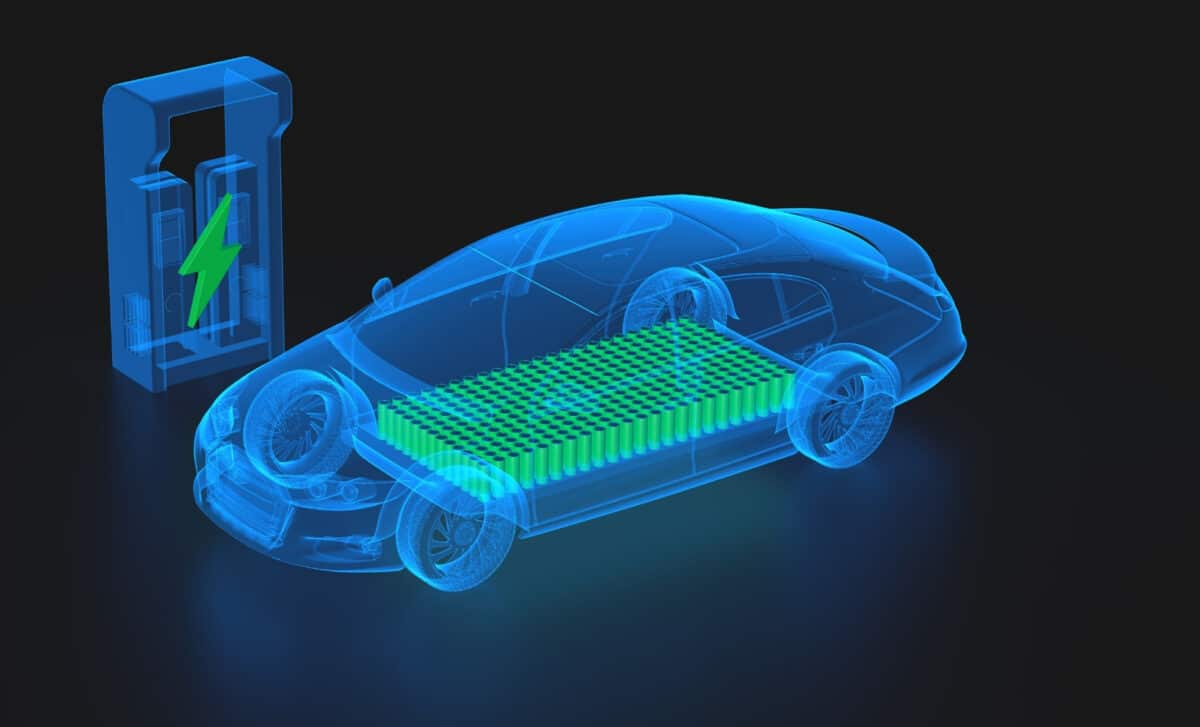
Surpassing the 1,000 KM Barrier
What sets this battery apart is its claimed range, which reportedly exceeds 1,000 kilometers per charge. For comparison, most current electric cars fall within the 500 to 600 km range under the WLTP cycle. This could more than double the distance possible on a single charge in some models.
The company has also focused heavily on thermal stability. The battery has successfully passed extreme heat resistance tests, including exposure to 200°C, without showing any signs of thermal runaway, a key safety concern in battery technology.
No official statement has been made about the exact WLTP-certified range or the models that will receive this battery first. Still, the figures released suggest a step change in autonomy, which would potentially allow drivers to travel from one end of many countries to the other without recharging.
Higher Energy Density and Safety Priorities
Energy density is another major talking point. The battery reportedly surpasses the 350 Wh/kg benchmark set by competitors such as Dongfeng. Hongqi’s design could reach up to 380 Wh/kg per cell, suggesting more energy stored in the same physical space.
While these figures have not been independently verified, they offer an indication of the technological direction pursued by FAW. Higher density means smaller batteries can offer longer range, and lighter systems could improve overall vehicle performance.
Looking ahead, 2026 will be dedicated to reliability testing under extreme climate conditions, an essential prerequisite before mass production. FAW has not disclosed pricing or commercial partners for deployment but confirmed that mass production is planned for the end of 2027, with market entry expected before the end of the decade.