The two-stroke engine was once a staple in vehicles like the Trabant and other older models. Its simplicity and lightweight design made it a popular choice, but its inability to meet emissions standards led to its decline. Despite this, Kawasaki has recently revived the technology for motorcycles, and now GM is taking an interest.
The new patent, filed with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, focuses on an innovation aimed at improving engine longevity and performance. While this could be seen as an engineering exercise, the decision to work on a two-stroke engine raises questions about GM’s future strategy.
A Bold Approach to an Old Problem
GM’s patent focuses on a key issue that has always plagued two-stroke engines: the rapid wear of engine segments. In conventional two-stroke engines, the cylinder walls wear down quickly because of the openings that handle intake and exhaust gases. The new GM system proposes a sliding sleeve inside the engine, which acts as a valve to control the intake and exhaust without exposing the engine segments. This innovation aims to increase the engine’s lifespan by minimizing wear on critical components, potentially solving a problem that has historically limited the engine’s use in cars.
However, even with this innovation, the two-stroke engine remains a challenging solution. While it could improve internal efficiency, it doesn’t address the fundamental issue that led to its abandonment: emissions. Two-stroke engines are notoriously less fuel-efficient and produce more pollution than modern four-stroke engines, making them unsuitable for the stringent environmental regulations of today. This challenge persists even with GM’s latest design.
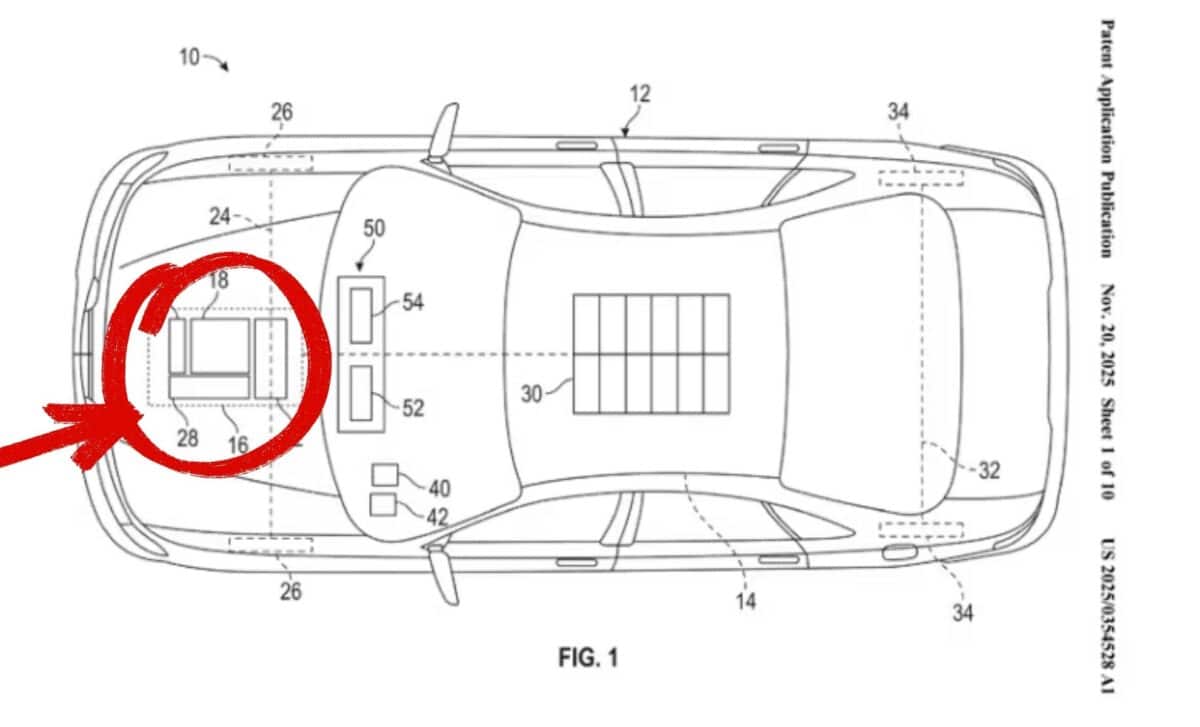
Why Now?
The decision to pursue a two-stroke engine may seem odd given the modern automotive landscape, which is heavily focused on reducing emissions and increasing fuel efficiency. According to industry observers, GM’s move could be a proactive approach to potential regulatory changes. With shifting political climates and the possibility of relaxed emissions standards in the future, particularly in regions like the U.S., GM might be preparing for a world where stricter environmental regulations are not as much of a constraint.
Nevertheless, GM’s work on the two-stroke engine might not lead to a mass-market product. Many companies file patents as a way to protect their ideas or explore technical possibilities without necessarily intending to commercialize them. In this case, GM’s recent patent might simply be an exercise in innovation rather than a step toward bringing two-stroke engines back into production.
The Future of Two-Stroke Technology
Despite the challenges, two-stroke engines are not completely out of the picture. While they have largely disappeared from the automotive market, they continue to thrive in other industries, like motorcycles, lawn equipment, and small engines. This resilience points to the possibility that two-stroke engines could make a limited comeback in specific niches, especially if they can be adapted to meet modern performance and environmental standards.
In the case of GM, their exploration of the two-stroke engine, even within the hybrid context, suggests they are keeping an eye on evolving technologies. However, the path to widespread adoption, especially in hybrid or fully electric vehicles, remains unclear. For now, GM’s two-stroke patent is just another piece in the puzzle of the future of automotive engineering, without any clear indication that it will ever reach the mass market.